⚡ Tl;dr
- The model code gap is the difference between the abstractions we use to discuss software architecture and the reality of the source code.
- Automated tools generate diagrams that are a 1:1 accurate representation of your infrastructure and source code, but they may not be as useful as you think.
- Abstractions are essential in software architecture to scale our conversations to large and complex systems.
🚀 Let’s kick-off
The model code gap is an idea from George Fairbanks’s book “Just enough software architecture.” It describes the conceptual gap between the abstractions we use to discuss software architecture (a model) and the reality of the executed source code.
The main characteristic of the model code gap is that if you attempted to automatically convert the model to code and back again, the output would mismatch. For example, an architect may prescribe that certain endpoints must have a maximum of 0.5-second latency, which wouldn’t be obvious looking at the source code. Even though source code must reflect and adhere to things such as architectural direction, design decisions and business requirements, it rarely explicitly defines them.
🖼️ Why are abstractions important
We commonly use abstractions to talk about software and choose an appropriate level of detail for the conversion. If you’re having a conversation about how different services or systems communicate, then talking about low-level functions will not help get your point across. We create higher-level abstract concepts to describe things such as services, logical areas of the system or communication protocols. This is essential to scale our conversations about large and complex systems without including the details.
For more on how abstractions help with technical conversations, see our blog post about abstractions in system architecture design.
🤖 Generating diagrams from code
Diagrams and documentation can often be a laundry task for developers; instinctively, we look for solutions to make the job easier. You’ve likely heard the following suggestion before. “Can’t we just generate up-to-date diagrams from our infrastructure and codebase?” In this idyllic world, you can press a magic button 👉🔘, instantly generating beautiful and informative diagrams that your team regularly uses to understand the software architecture. In theory, your diagrams will always be up-to-date and 100% accurate.
The reality of generating diagrams from code is that although you’ll generate diagrams that are a 1:1 accurate representation of your infrastructure and source code, they likely won’t be very useful for your team. The output visualizes such a low level of detail that it’s not particularly useful when discussing higher-level abstractions and concepts. The problem is that the tool generating these diagrams cannot cross the model code gap.
For example, see this diagram generated from AWS infrastructure (published by Markus Tacker). This is only the top part of the diagram 😅.
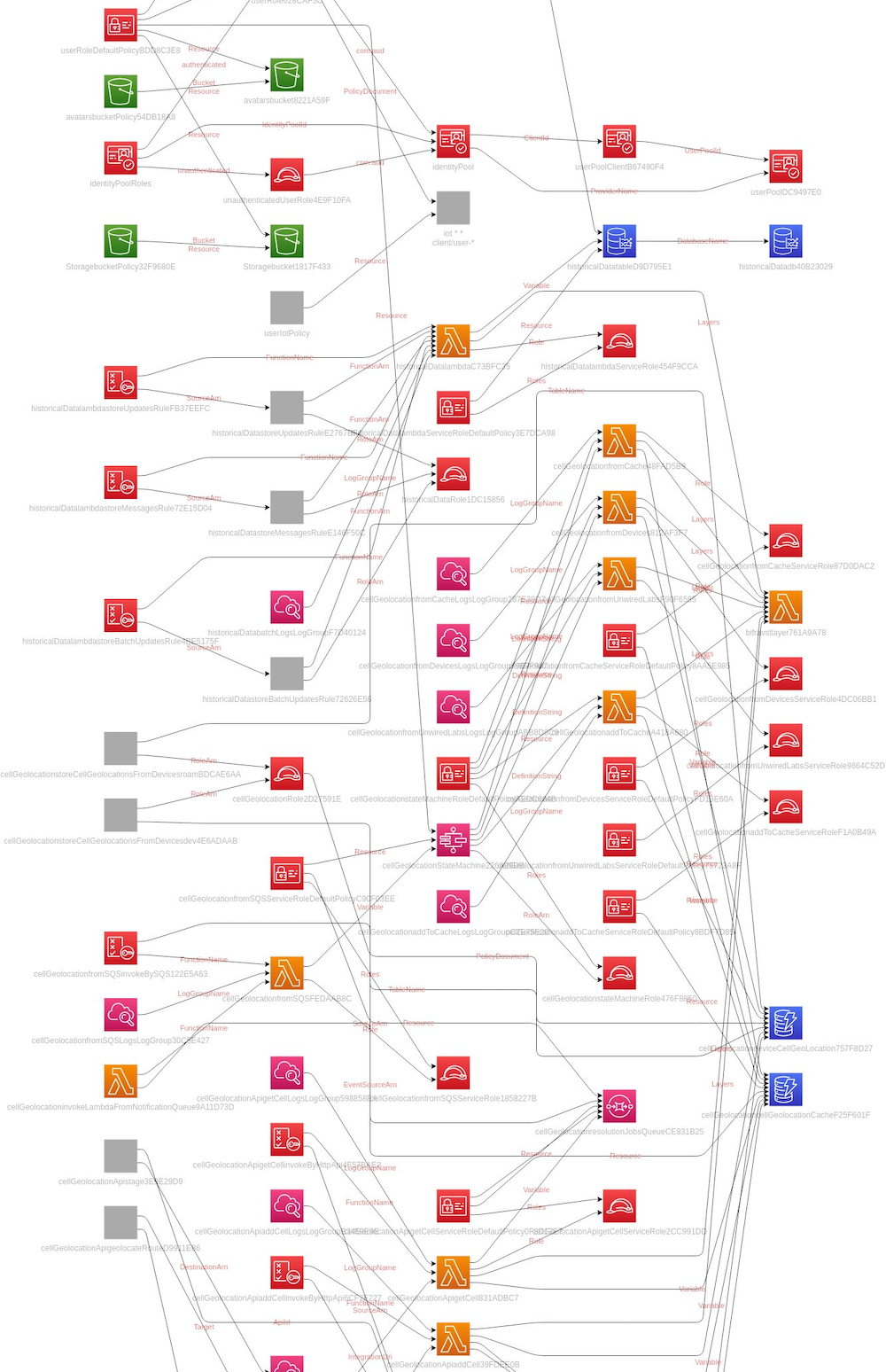
Rather than attempting to generate diagrams from the executable code or infrastructure, it’s more useful to start using abstractions and build a common language for your team. Tooling such as the Structurizr DSL can define abstractions and diagrams as code, although it may be far from the magical solution many developers hope for.
🏁 To wrap up
The gap between executable code and the abstractions we use to discuss systems is something many developers don’t realize and aren’t familiar with. Hopefully understanding this can prompt the right conversations for the proper use of abstractions for communicating system architectures across teams. And maybe think twice before generating diagrams from code 😉.
Stay chill 🧊